Traffic Sources
Every referral to a web site has an origin, or source. Possible sources include: “google” (the name of a search engine), “facebook.com” (the name of a referring site), “spring_newsletter” (the name of one of your newsletters), and “direct” (users that typed your URL directly into their browser, or who had bookmarked your site).
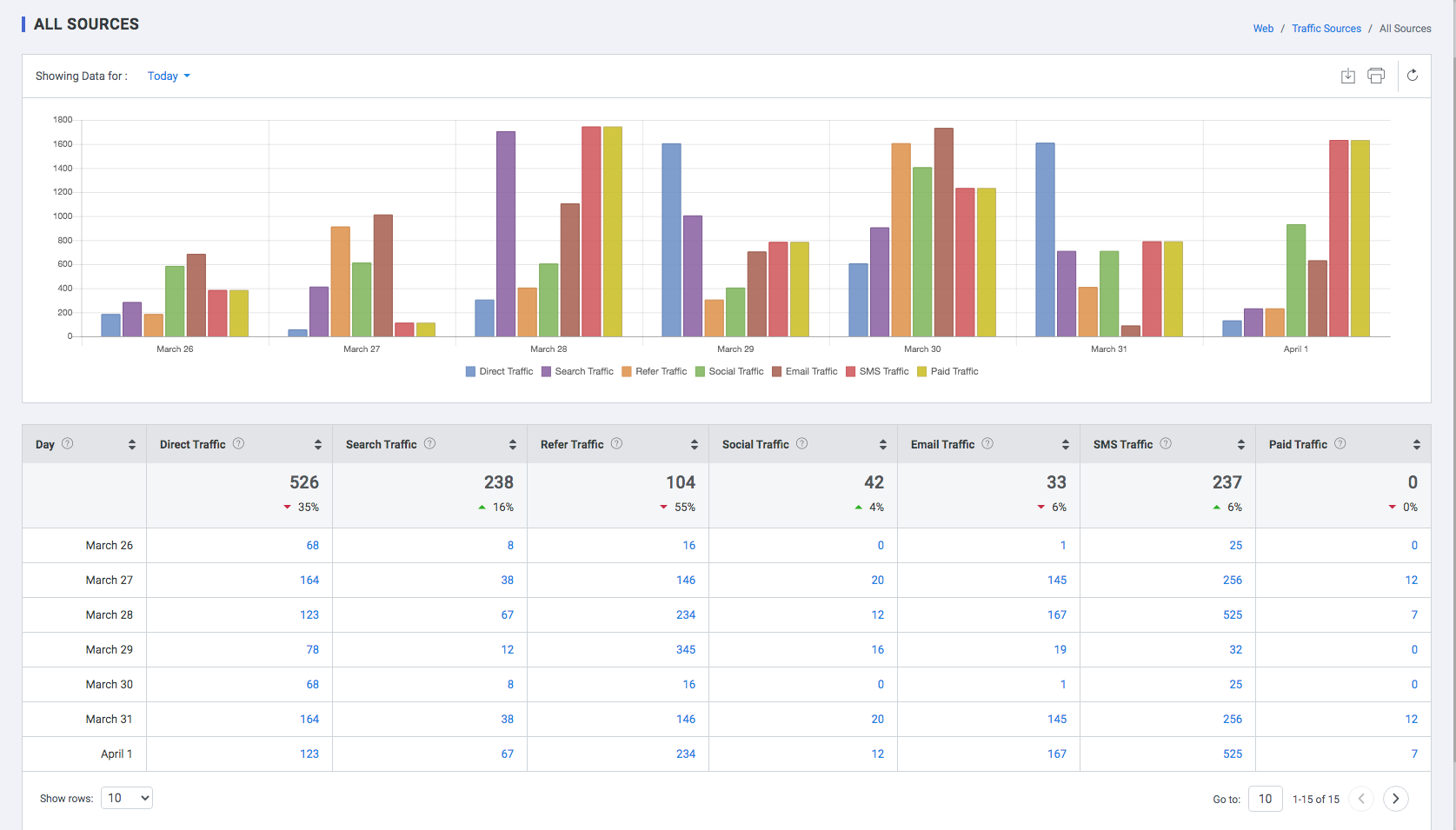
All Sources
A report that shows all origin of your traffic, such as a search engine (for example, google) or a domain (example.com)
- Direct Traffic: Direct traffic refers to the traffic that comes to the website directly by typing the website name.
- Search Traffic: Organic traffic that comes from different search engines like Google, Yahoo etc.
- Refer Traffic: Referral traffic is traffic that comes from various websites and other channels.
- Social Traffic: social media traffic is traffic that comes from Social media channels like Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, LinkedIn, Youtube, Instagram, and other social media links.
- Email Traffic: Email traffic is traffic that comes from Email campaign response.
- SMS Traffic: SMS traffic is traffic that comes from SMS campaign response.
- Paid Traffic: Paid traffic is the traffic you get from different channels like search engines or social media platforms by paying a certain amount of money.
| Field | Description |
| Day | Time, date and month of all the sources through which the visitors visited your website |
| Direct Traffic | Number of sessions of unique visitors which happened through direct source |
| Search Traffic | Number of sessions of unique visitors which happened through search source |
| Refer Traffic | Number of sessions of unique visitors which happened through refer source |
| Social Traffic | Number of users who logged into the website via social media like Facebook, Twitter etc. |
| Email Traffic | Number of sessions of unique visitors which happened via your email campaigns |
| SMS Traffic | Number of sessions of unique visitors which happened via your SMS campaigns |
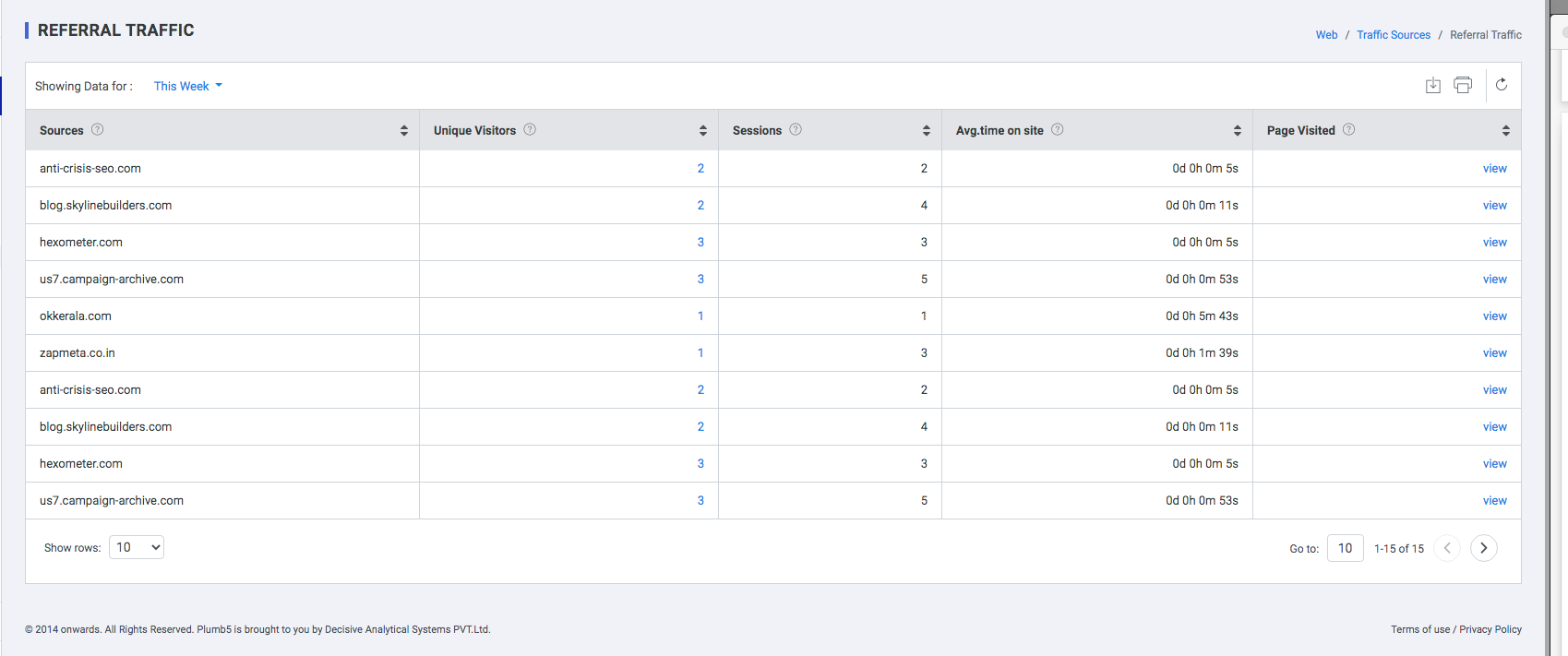
Referral
Referral traffic is a method of reporting visits that came to your site from sources outside of search engines. When someone clicks on a hyperlink to go to a new page on a different website, Plumb5 Analytics tracks the click as a referral visit to the second site. The originating site is called a “referrer” because it refers traffic from one place to the next.
| Field | Description |
| Source | Source website through which the user logged in |
| Unique Visits | Distinct visitors to the website on the date mentioned in the Day column |
| Page Depth | Number of pages viewed by the user |
| Avg Time on site | Average Time spent by the user in the website |
| Pages Visit | The pages visited by the user |
Referral reports allow you to measure the impact of social media traffic, PR placements, business listing sites, and other sites linking back to your own. By looking at traffic levels, user engagement, and goal completions, you can determine how well each site contributes to your bottom line. While incoming links bring other kinds of value to a site’s online presence, those sending referral traffic can have a direct and measurable impact on the bottom line.
Ultimately, you should tie referral data into your analytics reporting process to identify high-performing referring sites on which to focus future efforts. Using this data you can more easily pinpoint links coming from valuable sites, underperforming sites that show potential and low-quality listings that may not be worthwhile to continue.
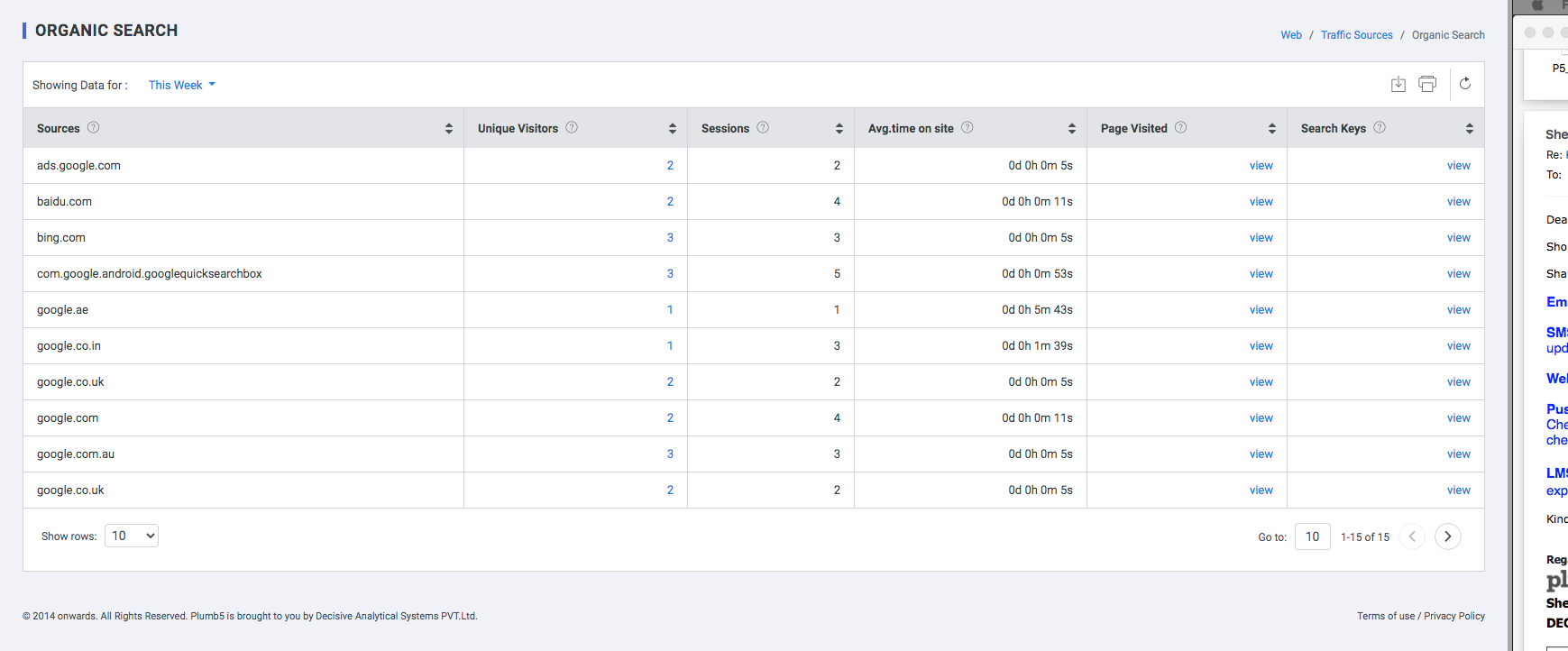
Organic Search
Understand and customize how organic searches are attributed. Plumb5 Analytics separates traffic that arrives at your site through a search engine result from traffic that arrives through other referring channels, like paid advertisement or another site that links to yours. In your reports, this traffic segment is called organic search traffic. For information on traffic types, read about traffic sources.
Plumb5 automatically recognizes the most popular search engines, and attributes traffic to these sources. Traffic that finds your site through any of the default search engines appears as organic search traffic in your reports. Traffic that finds your site through any search engine not included in this list is considered referral traffic, (not as organic search traffic), in your reports.
| Field | Description |
| Source | Source website through which the user logged in |
| Unique Visits | Distinct visitors to the website on the date mentioned in the Day column |
| Page Depth | Number of pages viewed by the user |
| Avg. Time on site | Average Time spent by the user in the website |
| Pages Visit | The pages visited by the user |
| Keys | The search keyword used to access the website |
Paid Campaigns
In the world of web analytics, Paid traffic is a form of referral traffic coming from search engines like Google, Bing and Yahoo. Or it can also be from the display ads of the search engines that come directly from a link on a different website. The traffic associated with a Campaign is traffic that has been tagged by the marketer.
Plumb5 automatically tags Paid mediums like AdWords, based on the ACLK and GCLID parameters passed as referrer pages before the visitor visits the landing page. For campaigns that do not have the above parameters in the url, a good practice is to manually tag your marketing campaigns so they are better segmented within Plumb5 – based on parameters passed in the campaign url using UTM Parameters.
The way you tag links is with UTMs. UTM tags are small snippets of text which appear at the end of a link. Below is an example of a UTM tagged link:
Example:
Marketers need to use UTMs on every single link that drives traffic to any of their web properties. If you don’t have access to the link – for example, if it’s a link in an email campaign being sent out by a partner – then send the UTMs to the partner and ask him or her to add them to the link. The more segmented your traffic the more you can learn about the different channels. In this section a brief summary of users who accessed the website through the advertisements is displayed in the following 3 sections
- Ad words
- AdSense
- UTM Tags
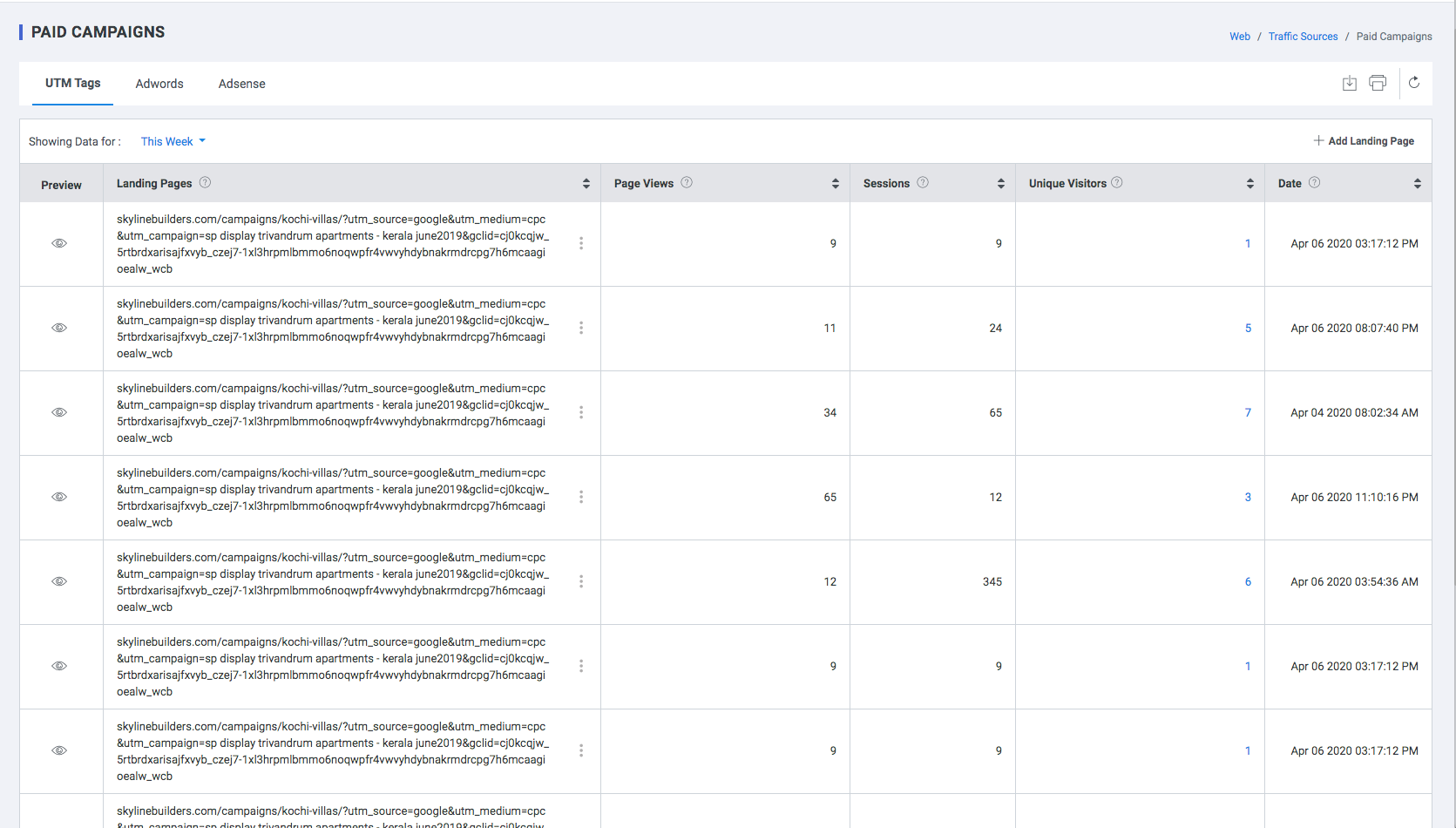
Add Landing Page
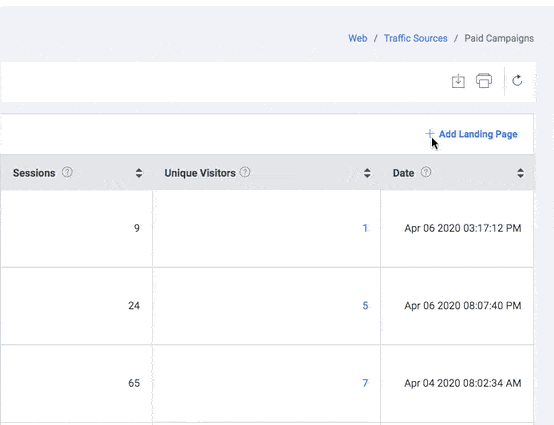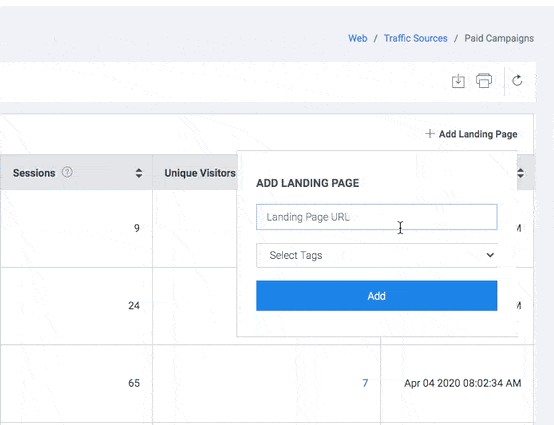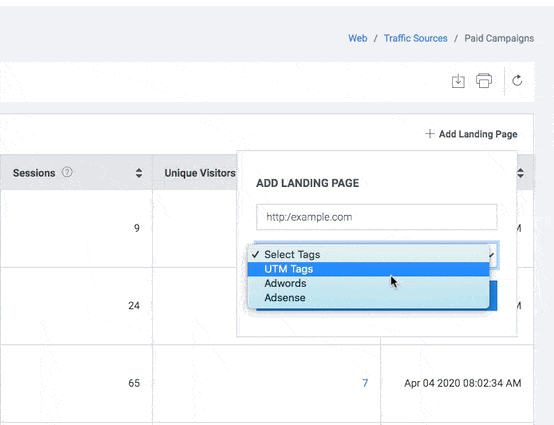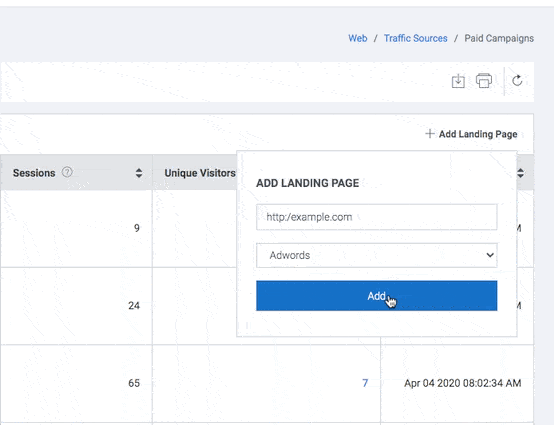
- Click the “+ Add Landing Page” button to add a new landing page. Add Landing Page is displayed.
- Enter the URL of Landing Page which the user would like to view frequently.
- Click Select Tags drop down to view the respective mode of advertisement.
- Click the SAVE button
Click delete option in the context menu to delete the respective landing page
Social Sources
This report on Social Network Referrals and Social Conversions provide great insight into the quality of the traffic your website receives from social media. To get the most out of these reports, make sure that you are properly tagging your URLs whenever you share content on social networks.
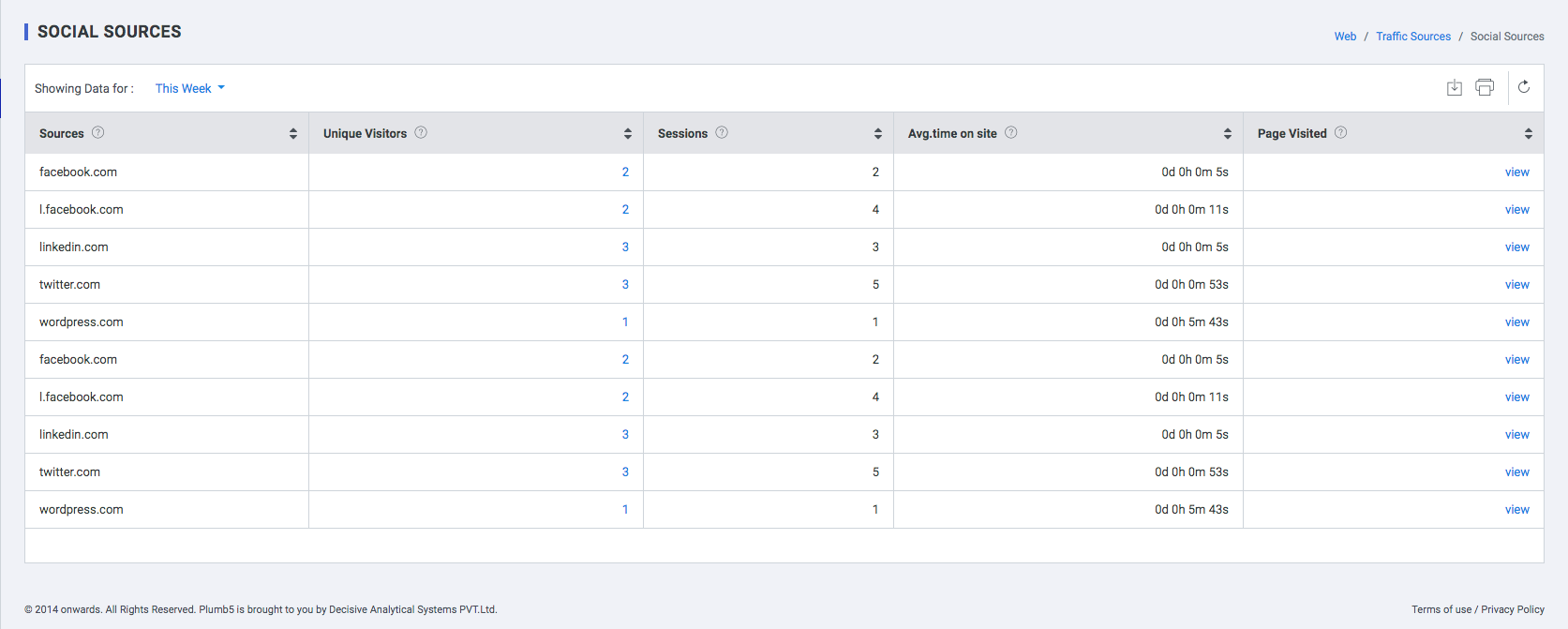
| Field | Description |
| Source | Social sources by which visitors gained access to the website |
| Unique Visits | Unique visitors who visited the website, using respective social sites, in a time frame defined by user |
| Avg. Time on site | Average Time spent by the user in the website |
| Pages Visit | The pages visited by the user |
Email Sources
This report on Email sources provides great insight into the quality of the traffic your website receives from your Email Campaigns.
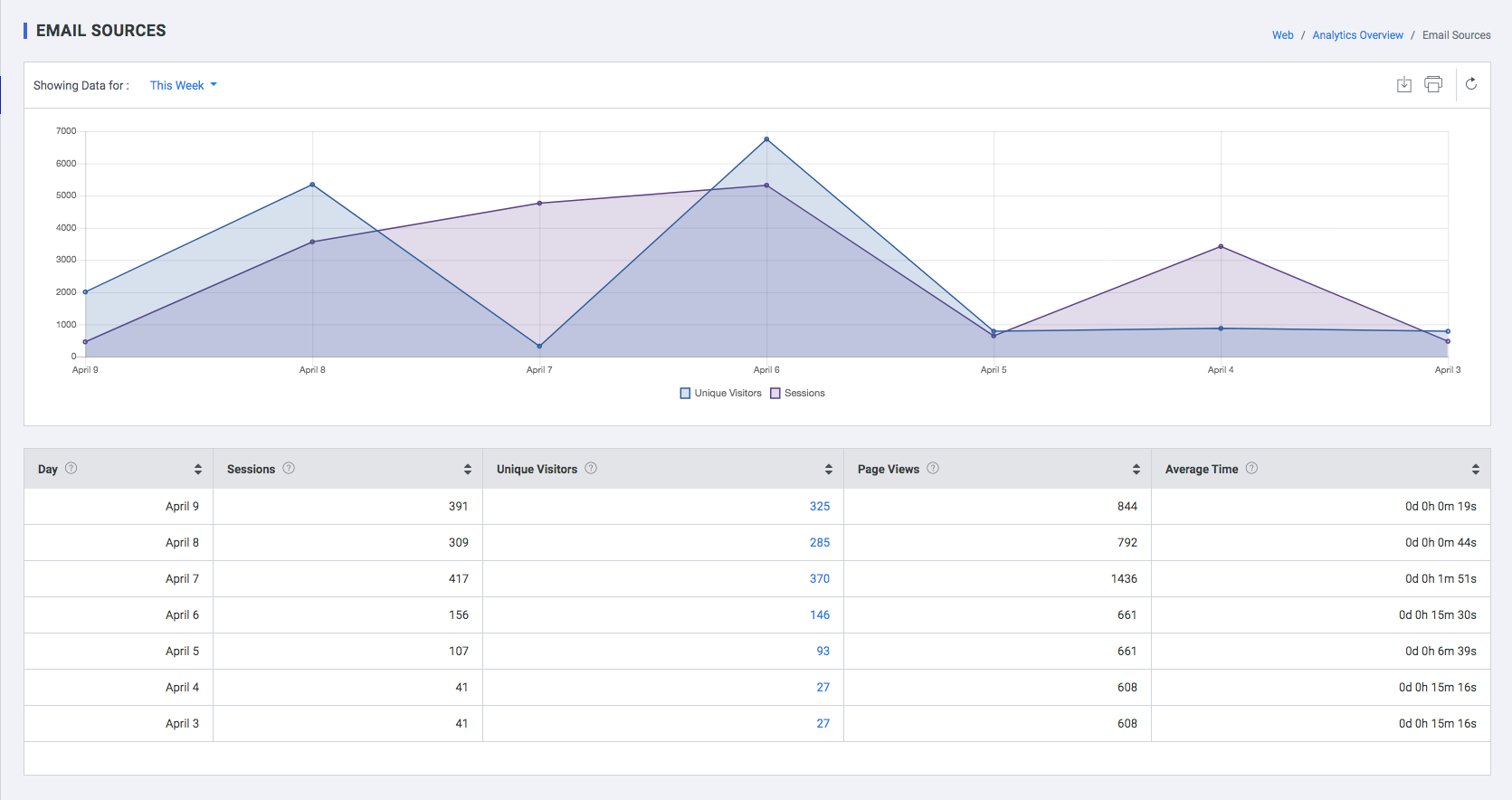
| Field | Description |
| Day | The date on which the user accessed the website |
| Sessions | Number of sessions which were initiated from an email |
| Unique Visits | Unique visitors who accessed the website via an e-mail, in a time frame defined by you |
| Page Views | The pages visited by the user |
| Avg. Time | Average Time spent by the user in the website |
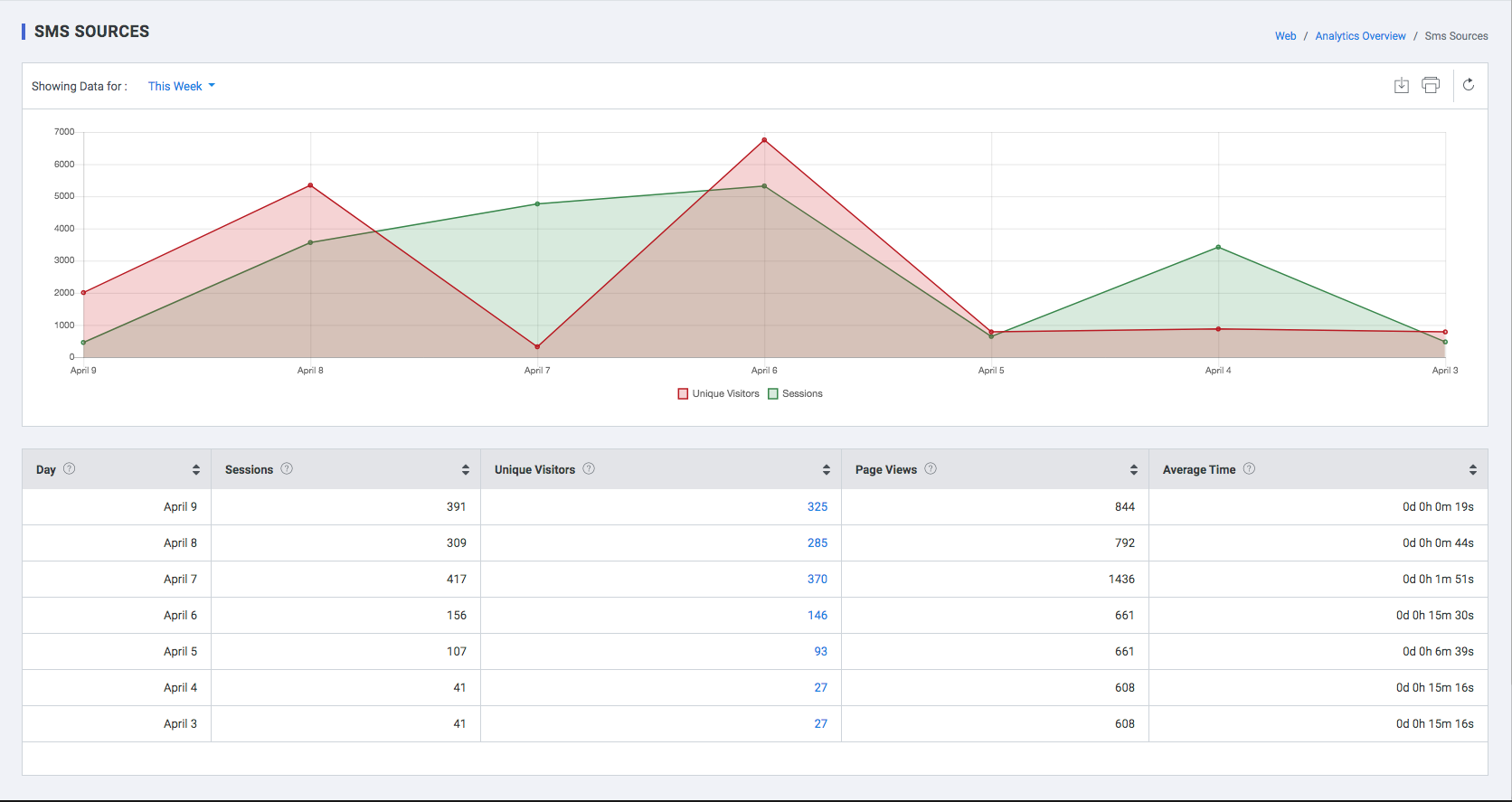
SMS Sources
- Using Bounce rate with Traffic sources
- Average time on site with Traffic sources
- Page Depth With Traffic Sources
- Frequency with Traffic sources
| Field | Description |
| Day | The date on which the user accessed the website |
| Sessions | Number of sessions which were initiated from an SMS |
| Unique Visits | Unique visitors who accessed the website via an SMS, in a time frame defined by the user |
| Page Views | The pages visited by the unique visitors |
| Avg. Time | Average Time spent by the user in the website |
Visitor Flow
Visualize your users' paths through your site. The Visitor Flow report is a graphical representation of the paths users took through your site, from the source, through the various pages, and where along their paths they exited your site. The visitor Flow report lets you compare volumes of traffic from different sources, examine traffic patterns through your site, and troubleshoot the efficacy of your site.
You can compare relative volumes of traffic from different sources within the same dimension: for example, the traffic from different search engines, campaigns, or mediums. Overall comparisons let you make some initial determinations about which channels are most effective or offer the best return
Depending on the purpose of your site, you may want to know how many pages users traversed after the initial page. Did they go right from product pages to checkout without any additional shopping?
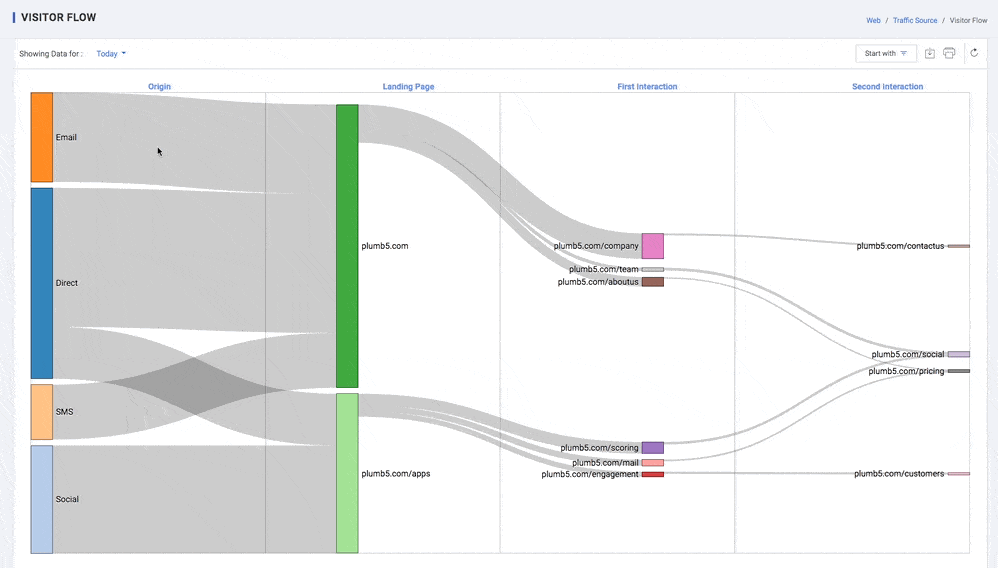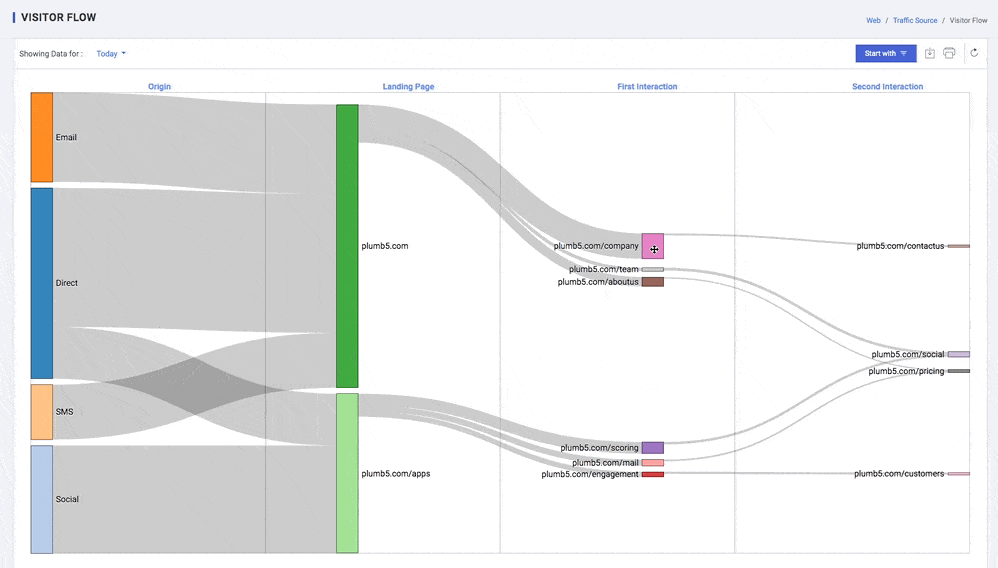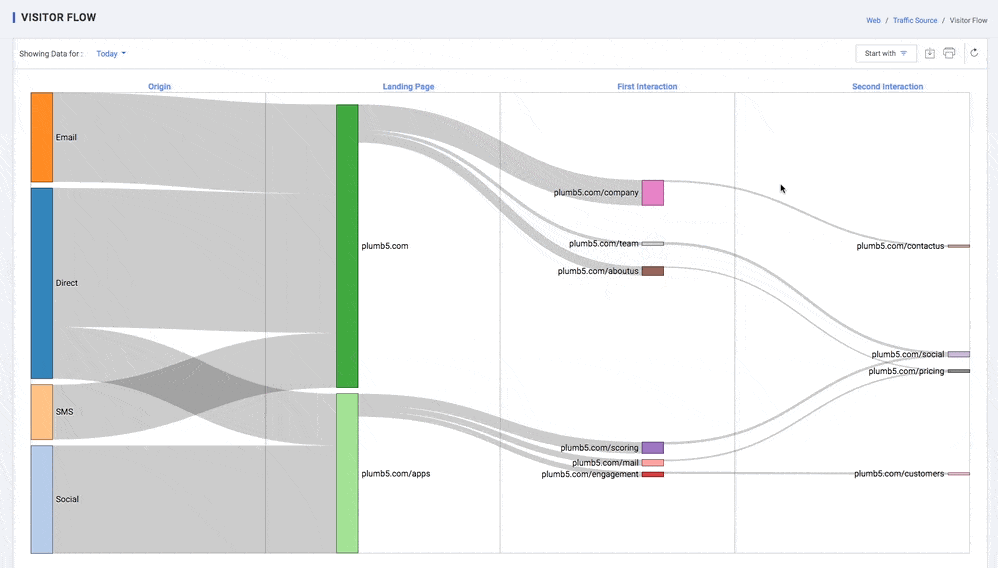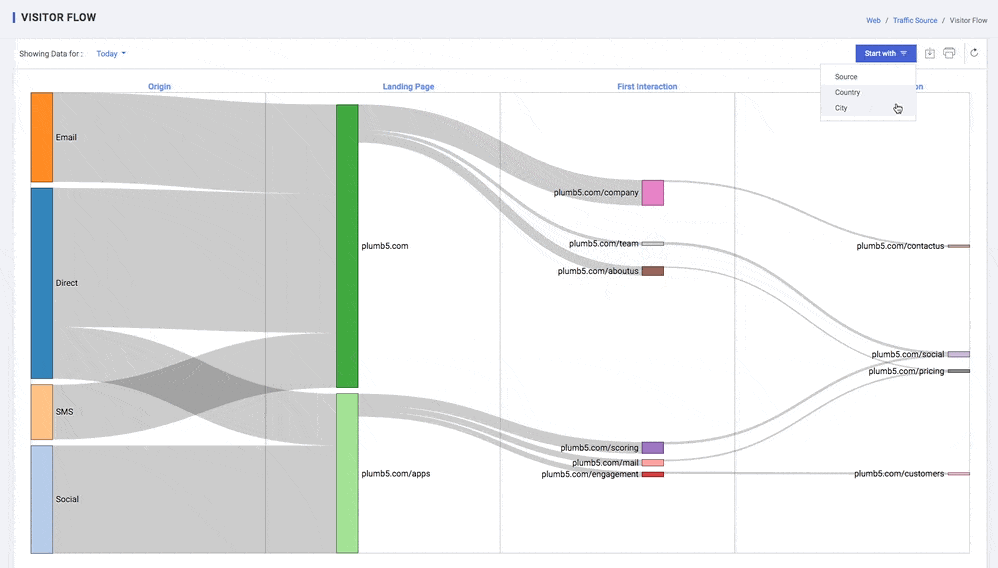
Structure of the Behaviour Flow report
- One value of the starting dimension by which you're filtering the visualization, e.g., Source, or Country or city. This type of node is found in the first column of either the Pages or Events view
- A single page or collection of pages, e.g., all pages in the wearables directory. This type of node is found in either the Pages or Pages and Events view
- A group of Pages and Events that you have grouped together by tracking code, extraction rules, and/or rule definitions. This type of node is found if you select a view for a Content Grouping you've set up
- An Event, e.g., a video play or download. This type of node is found in either the Events or Pages and Events view
- A connection represents the path from one node to another and the volume of traffic along that path. Click a connection to highlight just that traffic segment through the flow
An exit indicates where users left the flow. In Events view, exits don't necessarily indicate exits from your site; exits only show that a traffic segment didn't trigger another Event. Exits aren't currently shown in the Pages and Events view.